Feeding transition cows
3 min read
The transition period in a cow's life requires precise feed management to ensure health and optimal milk production. It’s important to set BCS targets, monitor those targets and adjust your feed budget as required, especially pre- and post-calving.
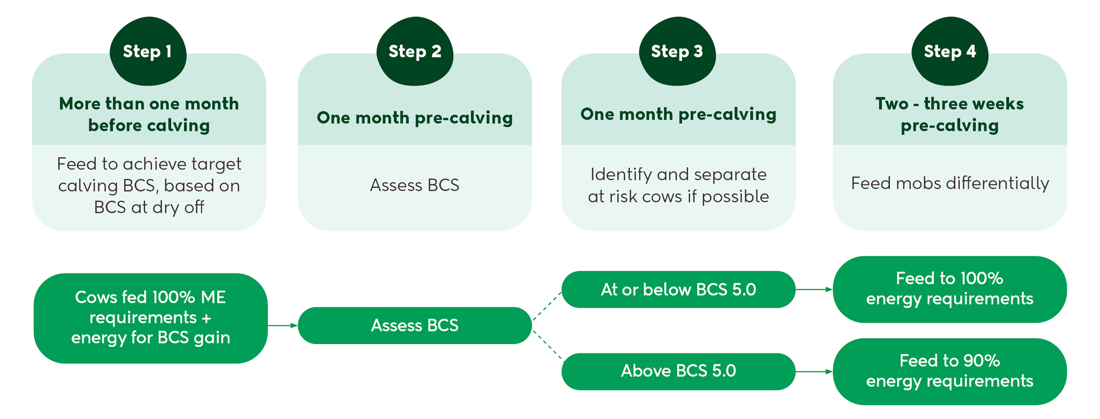
Focus on achieving BCS targets. Meeting BCS targets will simplify management of the transition cow pre- and post-calving. Although average BCS values for the herd are useful, it is important to identify individual cows that are at, above, or below target.
Cows need to be dried off in sufficient time to reach BCS targets before calving. Don’t wait until the last month pre-calving to gain BCS. Cows gain very little condition (even when fed generously) in the last month before calving because the energy requirements for maintenance and pregnancy are so high.
Avoid overfeeding cows pre-calving. In the two to three weeks pre-calving, a slight restriction can be applied by feeding 90% of energy requirements in cows that are above BCS targets.
Once BCS is determined pre-calving, cows that are at, above, or below targets can be managed acording to their BCS.
| Liveweight | ME requirement | DMI requirements kgDM |
| 350 | 76 | 6.9 |
| 400 | 84 | 7.6 |
| 450 | 92 | 8.4 |
| 500 | 100 | 9.2 |
| 550 | 107 | 9.7 |
Metabolisable energy (ME) + approx. dry matter intake (DMI) requirements 2-3 weeks pre-calving.
| Liveweight | ME requirement | DMI requirements kgDM |
| 350 | 85 | 7.7 |
| 400 | 94 | 7.5 |
| 450 | 102 | 9.3 |
| 500 | 111 | 10.1 |
| 550 | 119 | 10.8 |
Metabolisable energy (ME) + approx. dry matter intake (DMI) requirements 2-3 weeks pre-calving.
These are feed eaten figures and need to include wastage. Assumed ME content of diet = 11MJ/Kg DM.
Earlier recommendations to “steam up your springers” or feed as much as possible to pre-calving cows will result in greater BCS loss, reduced feed intake and increased risk of metabolic disorders post-calving.
It is important to note that individual cows within a herd that have a lower voluntary dry matter intake pre-calving (e.g. less than the herd allowance) may have an increased risk of metabolic and infectious diseases postpartum and should be monitored.
Choose feeds pre-calving based on cow energy requirements (MJ ME), and then feed cost and availability.
The type of feed pre-and post-calving will determine if feed composition, such as protein, fibre or carbohydrate type, are important considerations. Also, the composition of feeds and amount being fed can affect the mineral composition of the diet, which is important to consider for metabolic disorders.
In a predominantly pasture-based system, there is no benefit from increasing the proportion of non-structural carbohydrates in the diet pre-calving.
There is no need to feed extra sugar or starch pre-calving, unless cows will be eating a diet high in sugar and starch post-calving and require transitioning onto this diet.
Long chop fibre (e.g. hay, straw, silage) is required in the diet if cows are eating high levels of sugar and/or starch (e.g. fodder beet, swedes, maize grain, barley):
Prior to calving, cows require approximately 12% of their diet as crude protein:
During the colostrum period, cows should be offered unrestricted access to good quality pasture or supplements. These animals should be considered the top priority when it comes to allocating feed to different mobs. If cows are removed from high sugar or starch feeds (e.g. fodder beet) during the colostrum period, they will require re-transitioning if they are to continue eating this feed through early lactation.
Should I feed straw to my springers?
Straw can be used to reduce the energy content of the diet; however, it provides no nutritional benefits, unless the diet is high in sugar or starches.
Can you prevent BCS loss immediately post calving?
To adapt to the negative energy balance immediately post-calving, and provide the necessary energy for milk production, the cow mobilises large amounts of body tissue (primarily fat, with smaller amounts of protein), which results in a loss of BCS.
Little can be done in the first few weeks post-calving to alter this BCS loss. Increasing a cow’s energy intake will simply increase milk production rather than reduce BCS loss during this time. The primary regulators of the performance of the transition and early lactating dairy cow are BCS at calving, and nutrition management pre-calving.
For more information see:
Now’s the perfect time to check in, plan, and set up for a strong season. We’ve pulled together smart tips and tools to help you stay ahead all winter long.
Whether you prefer to read, listen, or download handy guides, we’ve got you covered with trusted tools to support your journey every step of the way.
Put our proven strategies and seasonal tools to work. Boost production, support animal health and watch your profits hum.
Tools that are backed by science, shaped by farmers and made for this season.
That’s Summer Smarts.
Autumn Smarts brings together the research-backed tools that build resilience and boost performance.