Spring management
8 min read
Spring management focuses on the critical period from calving through to your balance date when feed supply meets demand. Use our Spring Rotation Planner to manage the first grazing rotation after calving, achieving target average pasture cover, and balancing pasture allocation with cow intake to optimise whole-season performance. Successful spring management requires early identification and management of pasture surplus through weekly assessment and proactive use of tools like the feed wedge. This prevents ryegrass from forming stems and seed heads, maintaining feed quality for late spring and summer milk production.
In pasture-based systems, an optimum balance exists between daily pasture allocation and intake, and whole season performance. To achieve post-grazing residuals in spring (7-8 clicks), and promote maximum pasture growth and quality from the remainder of the season, a compromise is made between pasture growth and utilisation, and individual cow dry matter intake.
The Spring Rotation Planner tool takes the guesswork out, and puts the power of precise grazing management right at your fingertips over this critical period in the early spring.
There are 5 simple steps to calculate your optimal pasture allocation, ensuring you maximise every hectare during the critical post-calving period.
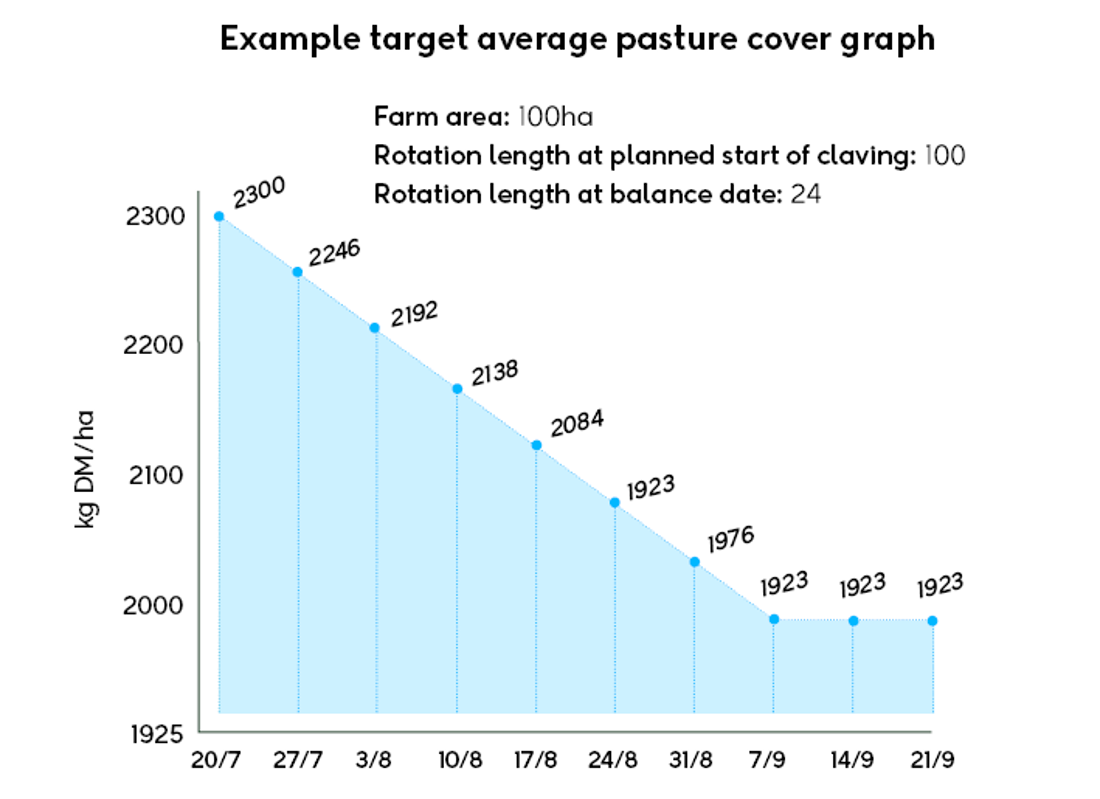
Achieving your target average pasture cover (APC) at calving is important for meeting feed demand, and for pasture growth rate and quality. APC at calving will determine how cows are fed for the first two months after calving. For more info see the APC at calving section on the pasture assessments page.
Graphing the average pasture cover you are targeting for your farm at any time between PSC and balance date means you can adjust your spring rotation planner for seasonal conditions that impact on pasture cover. You can create an average pasture cover graph as part of the spring rotation planner tool.
From the start of calving, the priorities are firstly the colostrum cows (as these are most prone to metabolic problems), then the milkers, followed by the springers and dry cows. The fastest way to have metabolic problems like milk fever or ketosis is to have well-fed springers and then underfed colostrum cows.
Feed intake potential at calving is significantly less than intake potential at peak. Cows can reach their peak milk production per cow in as little as 4 weeks after calving, but peak dry matter (DM) intake potential is not reached until 7-10 weeks after calving.
Although there are some good rules of thumb for individual cow intake, the best indicators to use collectively to determine if feed allocation and intake are adequate in a pasture-based system are:
Control of DMI in the early lactating cow involves many complex processes. There are several key animal and farm system factors that affect a cow’s intake or drive to eat. These include:
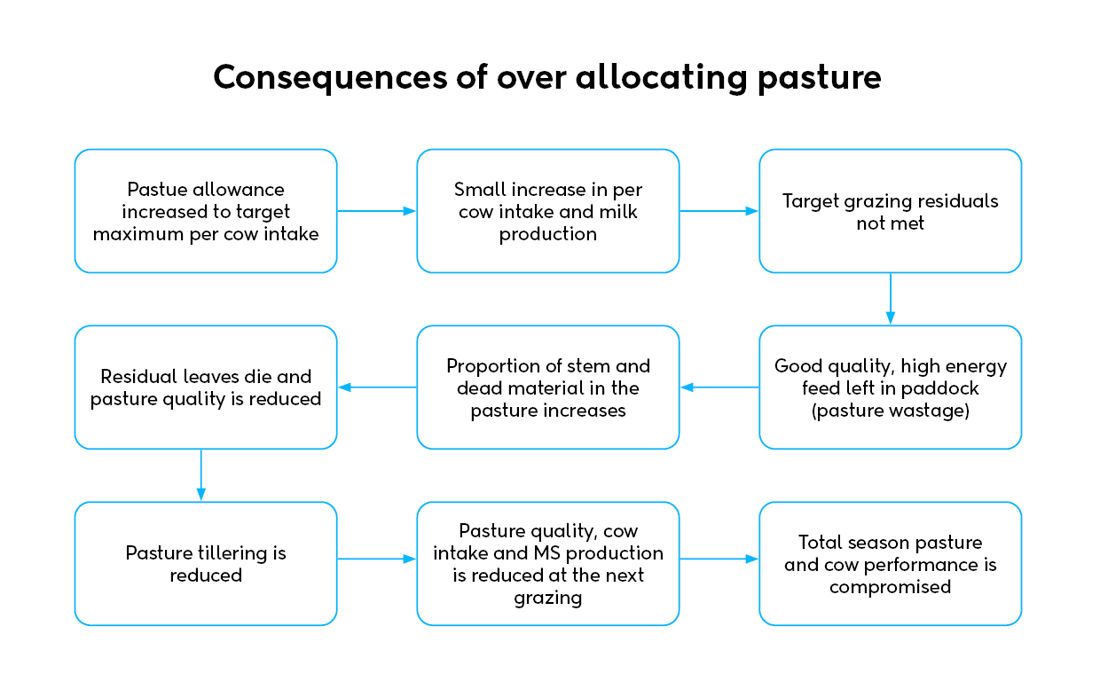
Pasture residuals are a good indicator of the adequacy of pasture offered (pasture allowance). Decisions on pasture allowance should focus on future pasture growth and quality and optimising whole season performance. There is a compromise between future pasture growth and utilisation, and individual cow intake.
Trials indicate cows (calving at appropriate BCS) can recover from a short-term moderate feed restriction in early lactation (75% of requirements/ residual 2.7cm for 14 days) with no negative effects on whole season production. If the restriction is more severe or the restriction lasts for a longer period, then there are both short- and long-term negative effects on milksolid production.
Decisions to use supplement feed during this period should consider the severity and duration of the feed deficit and the predicted response to supplement. Find out when supplements should be introduced as a tool to help maintain a slow rotation.
Ensure all feed allocated to your herd is of high quality this spring. High quality pasture contains more energy than many supplements. Scrutinise any supplement use – ensure you are getting a real benefit. Use supporting resources to ensure your information is correct.
Look for every opportunity to reduce wastage when feeding supplements; this improves milk production responses and helps bring down the cost of the feed eaten. It also makes feed reserves last longer.
When grazing residuals are less than seven clicks on the rising plate meter (1450kg DM/ha), supplements are an option. The return from supplements depends on the payout, the severity and length of time of the feed deficit, and the quality and utilisation of the supplement as shown in Table 1.
| Response | Residuals & APC | Supplement | Other |
| g/kg DM 11ME | |||
| >0 to 30 | 9.5 clicks or 1800kg DM/ha. At or above APC target | Quality < 10.5 ME; Wastage 30% plus (fed in wet weather; poor stack mgt) | Pasture quality in subsequent rotations poor & less pasture grown |
| 40-55 | 8-9.5 clicks (1600-1800kg DM/ha); stop feeding at target APC | Average quality 10-10.5 ME; Wastage 25%-30% | Supplement feeding stopped too late creating surplus |
| 60-80 | 6.5-7.5 clicks (1350-1550kg DM/ha if supplement not fed; residuals <8.0 clicks when supplement fed | Good quality 10.5-11.0ME; Wastage 20% or less | Short term feed deficit (<10days). Supplement feeding stopped before APC cover target achieved |
| 90-130 | Residual < 6 clicks (1350kg DM/ha) if supplement not fed. When supplement fed residuals 6-7 clicks (1350-1500kg DM/ha); APC well below target (> 300kg DM/ha deficit) | Good quality > 10.5 ME Low wastage 15% or less (feeding maize or PKE in bins/on feed pad) | Cows grazing to < 6 clicks for 10 days plus; supplement feeding stopped in anticipation of target cover being met. Responses increase with the period of severe underfeeding (8.0g/ME at least 2 weeks; 10g/ME 4 weeks; 12g/ME 5 weeks) |
In addition to the main minerals that may be required in early lactation (calcium, and magnesium) five trace elements are likely to be deficient in grazing dairy cows and are recommended for supplementation for 2-3 weeks pre-calving until 4 months post-calving.
These are copper, cobalt, selenium, iodine, and zinc. Consult a veterinarian to determine mineral requirements in your herd.
Identifying and managing pasture surplus early and maintaining good quality pasture through good grazing practices is key to maximising late spring and summer milksolids production.
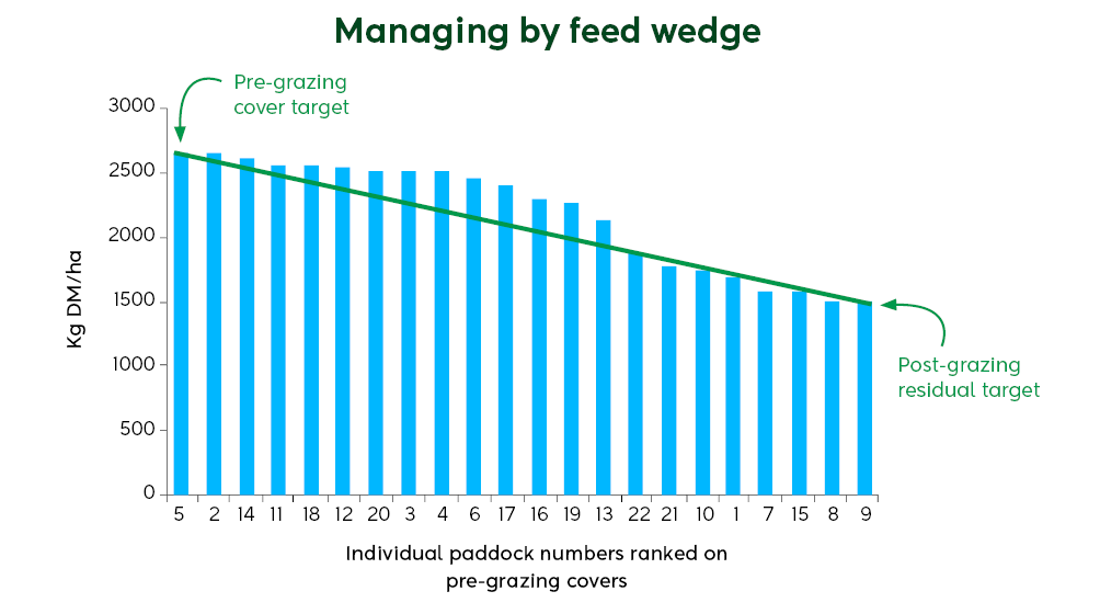
After balance date, the feed wedge is the best tool to manage pasture. A feed wedge shows the current pasture situation by ranking the paddocks based on average pasture cover. It allows you to make proactive decisions to manage a surplus or deficit.
Surplus management is one of the greatest skills of pasture management and is critical to maximise pasture eaten and feed quality. A temporary pasture surplus, if not managed, allows ryegrass to grow to form stem and seed head, resulting in lower pasture quality.
Pasture management in late spring is based around providing high-quality feed to the cows. Grazing residuals drive pasture quality, and when growth exceeds demand, residuals will rise unless this surplus is managed.
Surplus management is all about anticipation. To get surplus management right requires weekly pasture assessment to predict feed surpluses before they happen.
Identifying pasture surplus early allows better management of a surplus, including decisions around rotation length, removal of supplements and the number of paddocks to shut up. It also provides time to organise a contractor and therefore better control silage quality.
It is critical to anticipate in advance the length of the closed period and associated risks. These include:
For information, see the surplus management page.
Pasture silage is an important source of supplementary feed on New Zealand dairy farms. The better the silage’s quality, the higher the milksolids (MS) production and body condition score (BCS) gain in cows.
Good decisions with spring pasture
Pasture cut for silage must be of high quality and grazing residuals should be 1500-1600kg DM on paddocks to be closed for silage. Silage paddocks should be closed for no longer than six to seven weeks.
Cutting, packing and covering the stack must be done quickly to reduce spoilage losses. Some inoculants can improve the fermentation process. Take care to minimise losses both at the stack and in the paddock/feed pad.
Clover ryegrass mix
A good clover-ryegrass mix is vital for productive pastures. The core elements of productive pastures are best met by mixtures of ryegrass and white clover.
When clover comprises between 10 and 40 percent of total dry matter (DM) in summer, there are gains in DM of between 1.4 and 3.4 t DM/ha per year. Yield gains come mostly in summer, when extra feed grown has high economic value.
White clover generally requires higher levels of soil nutrients than ryegrass – especially phosphorus, potassium, sulphur and sometimes magnesium and molybdenum.
Excessive focus on nitrogen (N) fertiliser and failure to meet the soil nutrient requirements of white clover in recent years have inhibited clover growth and compromised pasture productivity.
For more information, read ‘Good clover-ryegrass mix – vital for a productive pasture.’
Grazing management
Spring grazing management influences the amount and quality of pasture grown later in the season.
Pasture quality is optimised when pastures are grazed between the 2 and 3-leaf stage of regrowth, and grazed to residuals of 3.5-4cm (or 7-8 clicks on RPM). Good pasture management in spring increases tillering in perennial ryegrass.
For more information, read Making the right decisions with spring grazing.
Spring to summer transition
Pasture response relevant to ryegrass persistence
Good management: improved persistence
Bad management: reduced persistence
Recommended rotation length: Shift from 20 towards 30 days.
Recommended grazing residuals
Note: grazing residuals are expressed as height in clicks, as measured by the rising plate meter based on the winter formula.
Now’s the perfect time to check in, plan, and set up for a strong season. We’ve pulled together smart tips and tools to help you stay ahead all winter long.
Whether you prefer to read, listen, or download handy guides, we’ve got you covered with trusted tools to support your journey every step of the way.
Put our proven strategies and seasonal tools to work. Boost production, support animal health and watch your profits hum.
Tools that are backed by science, shaped by farmers and made for this season.
That’s Summer Smarts.
Autumn Smarts brings together the research-backed tools that build resilience and boost performance.