Effluent system design or upgrade
3 min read
Farm dairy effluent systems manage waste from your dairy farm. Choosing the right system requires professional advice, considering future plans, and picking the right person for the job. You'll find diagrams and information in the page to help pick a system suited to your farm's needs, including factors like landscape, climate, and soil type. This page also guides you on the effects of landscape and climate on effluent management, soil assessment techniques, effluent technology and tools, energy capture systems, and using recycled dairy effluent water. If you're thinking of upgrading part of your system, you'll find specific resources here.
When making the decision to install or upgrade a farm dairy effluent system it's important to ask the right questions, gather information and take professional advice.
You want the system to work well for many milking seasons to come so it's important to consider the following:
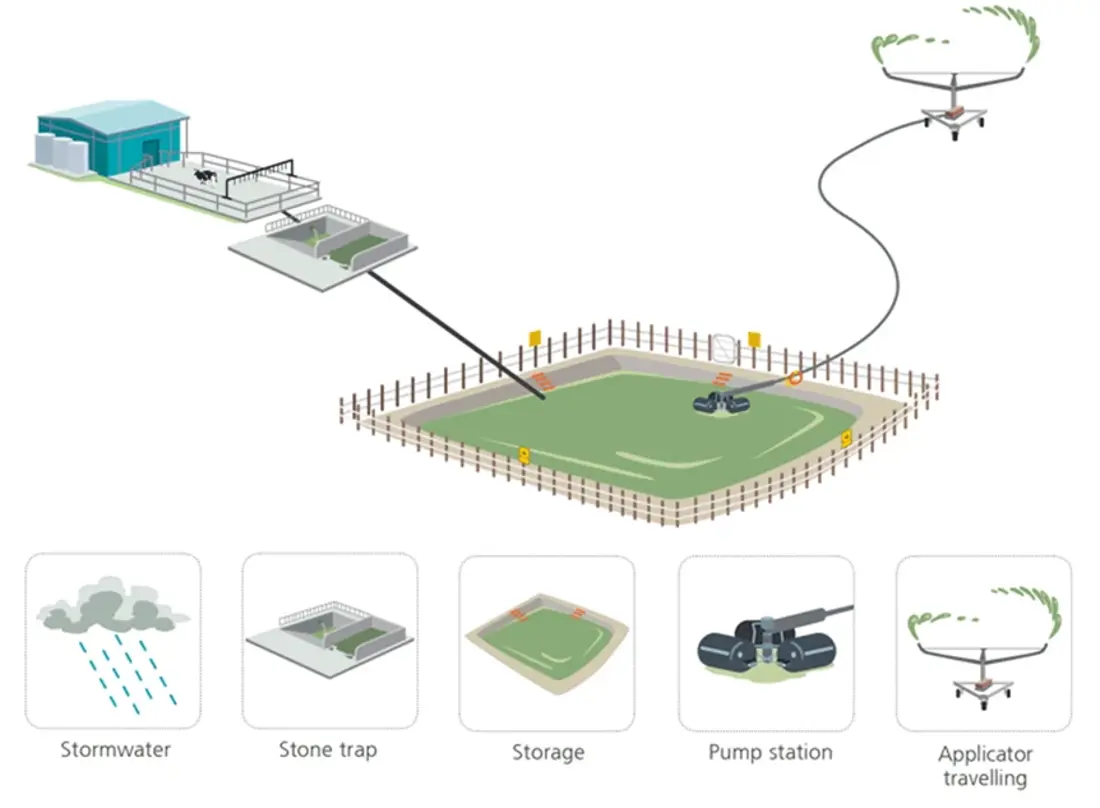
This system is the traditional design with a stormwater diversion in place at the yard. The effluent flows from the yard through a stone trap to a storage facility either via gravity feed or pump. It is then irrigated to land using a travelling irrigator.
Best suited for
Farms - With no particular landscape /climate / soil risk factors
Soils - Freely drained soils
Slope - Flat ground to gently sloping
Labour - Moderate labour input
Capital investment - Low to moderate (storage additional)
Other - Ideal for regular shaped paddocks
This system has a storm water diversion at the yard. The effluent then flows through a stone trap to a mechanical separator where the solids are removed. The liquid is then pumped to storage and irrigated to land via a small number of low rate applicators that are moved frequently.

Best suited for
Farms - That require flexibility in application depth and rate, such as high risk soils, high rainfall areas or sensitive catchments
Soils - All soil types. Especially suited to poorly drained or artificially drained soils
Slope - All
Labour - Higher labour input
Capital investment - Moderate to higher (storage additional)
Other - Works well in small or irregular paddocks
This system would typically include a storm water diversion then flow through a stone trap to a storage facility. A pump station is required if there is no gravity to storage. Effluent is stirred and sucked from storage into a muck spreader truck and sprayed to land.

Best suited for
Farms - Smaller farms and lower cow numbers, or when applying effluent to remote areas
Soils - All
Slope - Flat to sloping
Labour - Moderate to higher labour input
Capital investment - Lower (storage additional)
One of the most crucial aspects to consider is how landscape and climate affect effluent management. The main factors which play a role in the success of effluent application are:
See How landscape and climate affect effluent management for more information.
Management practices need to be matched to soil and landscape risk in order to prevent loss of effluent into the surrounding environment.
Soils across New Zealand have been classified into high and low soil risk categories for farm dairy effluent application.
The Pocket guide to determine soil risk for FDE application will take you step by step through the process of working out the soil risk for a farm.
New technology allows for the development of tools and programs to help with effluent, water, and nutrient management decisions on farms. Many expensive regional council fines can be avoided if a fail-safe device is installed on their irrigator.
There are several companies developing dairy effluent treatment systems that they believe will offer options for farmers, but these need to be carefully evaluated.
The Dairy Effluent Treatment Systems technical note provides a summary of relevant technical information as well as regulatory requirements that all parties need to consider before embarking on such a system.
Recently there has been interest in biogas capture from dairy effluent and converting to electricity for use on farm and/or selling to the grid. The Energy Capture Systems from Dairy Effluent technical note gives a brief overview of energy capture systems (both anaerobic digestion and biogas) from dairy effluent.
It has been developed for farmers and for companies looking to offer this technology to dairy farmers with assistance from experts around New Zealand. This technical note is essential reading before considering installing such as system on your farm.
It’s often a good idea, although there are strict food safety regulations that you need to understand and manage to prevent any possible risks to food safety. See Using Recycled Farm Dairy Effluent Water for Yard Wash-Down for guidelines.
For more in-depth information on solids separation systems see Part 2 in IPENZ Practice Note 27 - Dairy Farm Infrastructure.
All effluent systems designed for land application must be done in accordance with the Farm Dairy Effluent Design Standards and Design Code of Practice.
These resources contain all the technical specifications for a land application system. They are designed for companies designing effluent systems and for farmers who are technically savvy.
Now’s the perfect time to check in, plan, and set up for a strong season. We’ve pulled together smart tips and tools to help you stay ahead all winter long.
Whether you prefer to read, listen, or download handy guides, we’ve got you covered with trusted tools to support your journey every step of the way.
Put our proven strategies and seasonal tools to work. Boost production, support animal health and watch your profits hum.
Tools that are backed by science, shaped by farmers and made for this season.
That’s Summer Smarts.
Autumn Smarts brings together the research-backed tools that build resilience and boost performance.